





Metathesis reactions are reactions where the electronic environments of the atoms (caracterized by their oxidation numbers) do not change fundamentally.
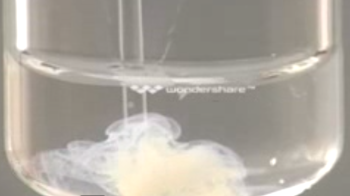
You see the reaction between silver ions $Ag^+$ and iodide ions $I^-$ : Initially free in aqueous solution, as soon as they enter in contact, these ions associate mutually to form an ionic lattice . A precipitate appears:
$Ag^+(aq)$ $+$ $I^-(aq)$ $\longrightarrow$ $Ag^+Cl^-(s)$
$(aq)$ means dissolved in water $(s)$ means a solid precipitate The symbol $+$ means that the ions are initially dissociated