







Principle
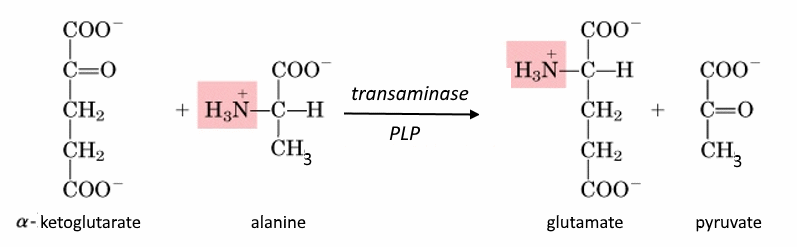
Specific enzymes for each amino acid, called transaminases, catalyze the transfer of the amino (or ammonium) group from an amino acid to the $ \alpha $ position of an $ \alpha $ -ketocarboxylate

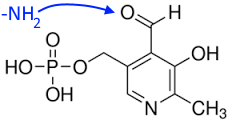
Transaminases are often "aided" by a "co"enzyme, pyridoxalphosphate (PLP, Vitamin B6), which is charged temporarily with the amino group by exchanging it on its aldehyde site:
Alanine
Aspartic acid
