





Oxidation product is the ethanoic acid. Ethanal and ethanoic acid have identical oxidation numbers of all corresponding atoms, except those of C:
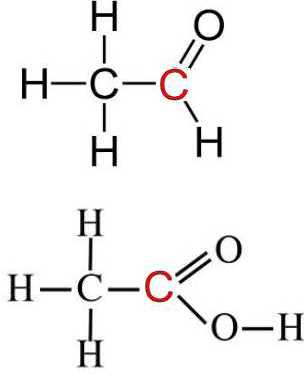
Reminder: Oxidation numbers are determined by attributing to the more electronegative atoms all of the electrons in the bond, and considering the dummy load thus obtained.
Aldehyde $\Rightarrow$ carboxylic acid $RCHO$ $-$ $2e^-$ $+$ $H_2O$ $\rightarrow$ $RCOOH$ $+$ $2H^+$
Product is the ethanoate ion. Ethanal and ethanoate ion have identical oxidation numbers of all corresponding atoms, except those of C:
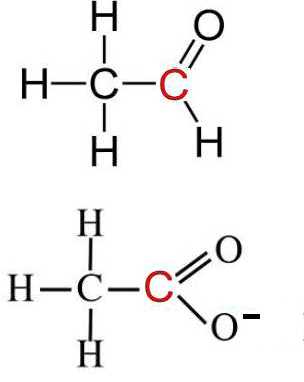
Aldehyde $\Rightarrow$ carboxylate $RCHO$ $-$ $2e^-$ $+$ $3OH^-$ $\rightarrow$ $RCOO^-$ $+$ $2H_2O$
Under stringent conditions, oxidation occurs with rupture of the molecule, otherwise there is no oxidation.
Ketones do not undergo controlled oxidation.